The Thuraya network has the area code: +88216.
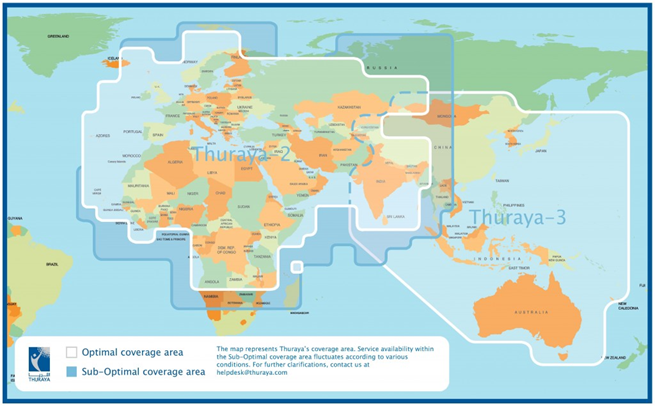
The Thuraya satellite network is operated with 2 satellites on a geosynchronous orbit about 36,000 km above the equator, whose coverage areas include 140 countries and are divided into 200 spot beams (focused radio areas). Assignment to the correct spot beam is based on the phone’s GPS position. For geosynchronous satellites, the apparent location of the satellites in the sky is not fixed as it is for geostationary satellites, but varies slightly throughout the day. Therefore, the transmit power levels fluctuate at the edges of the coverage areas.
Tip: On the page dishpointer.com you can determine the exact position of the Thuraya satellite for your location. There you select the satellite “44E Thuraya‑2” and enter the desired location or allow access to your current location.
The satellite Thuraya‑2 covers Europe and Africa. If you are in Asia/Australia, please select the satellite “98.5E Thuraya‑3”.

For calls within the Thuraya network, the connection is routed to earth via the gateway (ground station) in Sharjah (UAE). For calls to or from fixed and mobile networks, calls are routed from this gateway to terrestrial lines.
On a high transmission power “Sat-Alert” channel, the phone (even with the antenna folded in and in an unfavorable location) is first alerted to an incoming call (HPA High Penetration Alerting), the user then moves to a location with a clear view to the satellite’s position (in Europe mostly to the southeast). Now the phone logs onto the spot beam assigned according to the GPS position. The coverage zones can be shifted by changing the spot beam configuration. For example, after the Thuraya 2 satellite (Indonesia), which covers parts of Asia, went into operation, the coverage zone in Africa was improved by changing the spot beams of Thuraya 1 (off the coast of Somalia).
The built-in GPS receiver is on the one hand necessary for establishing a connection to the satellite, but can also be used for own location determinations, e.g. for emergency calls and tracking.
Since Thuraya uses a protocol derived from GSM (mobile telephony), this system is very similar to normal GSM usage, only with a bit more delay. The GmPRS (Geo Mobile Packet Radio Service) data channel provides higher rates than Iridium phones, namely 60 kbps download and 15 kbps upload. The GmPRS data service is packet-based and is therefore charged according to data volume.
About the history of Thuraya
Thuraya was founded in 1997 with headquarters in Sharjah in the United Arab Emirates. Its shareholders include Arab telecommunications companies (such as Etisalat and Arabsat) and investment firms (such as the Abu Dhabi Investment Company and Dubai Investments), as well as the T‑Systems company DETECON.
The satellites were manufactured by Boeing (Hughes) and, with a launch weight of more than 5.1 tons, are among the heaviest communications satellites in the world. They were launched using Zenit-3SL (Sea Launch) rockets. The antennas have a diameter of 12 meters. Due to the size of the antenna and a strong transmitting power as well as a high receiving sensitivity, the cell phones can be relatively small although they are far away from the satellite.


