The Inmarsat network has the area code: +87077.
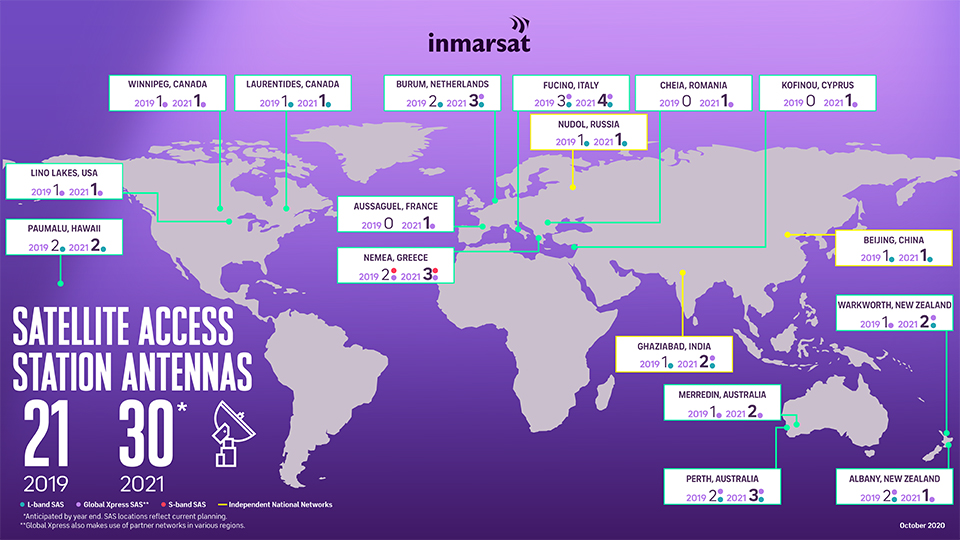
The Inmarsat satellite network is operated with currently 14 geostationary satellites in orbit at an altitude of 35,786 km and provides voice, data and emergency services on land, at sea and for air traffic via the L‑band, Ka/Ku-band and S‑band frequencies. The satellite network is connected to the Internet or fixed and mobile networks via 17 Satellite Access Station (SAS) and one Central Network management Centre (NOC) in London. Coverage currently extends between the polar circles. With the GX10A and GX10B satellites planned for 2023, the polar ice caps will also be covered for the first time, although not for all services.
All Inmarsat devices provide a built-in GPS module. Before the device registers with the Inmarsat satellite, it must first determine its GPS position and report it to the satellite.
Network coverage
To establish a connection to the satellite, a clear view of its position is mandatory.
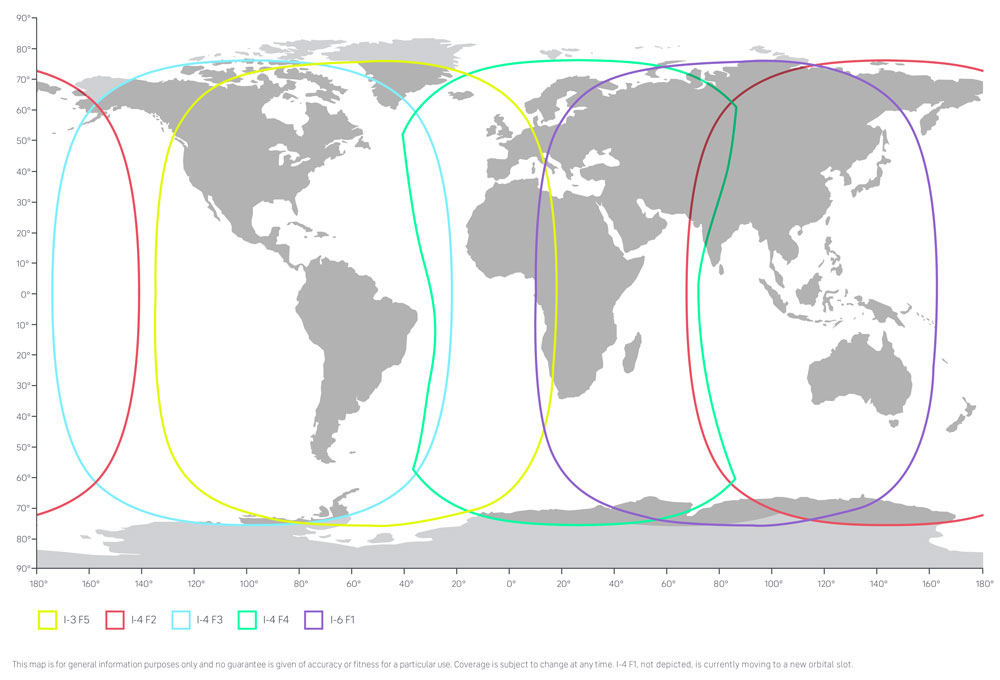
Each I‑4 satellite generates 19 wide coverage regions and more than 200 smaller focussed coverage areas. These coverage regions can be quickly reconfigured and focussed anywhere on earth to provide additional capacity when needed. For Inmarsat BGAN services the I‑6 satellites and their coverage are applicable:

Network coverage in detail
The DishPointer allows you to determine the exact position of an Inmarsat satellite for your location:
To do this, enter the desired location on the left or allow access to your current location.
In the list on the right, select the satellite closest to your location:
- 24.8E ALPHASAT for Europe, Middle East and Africa (refers to I‑4 F4 on the coverage map above)
- 63.9E INMARSAT 4‑F2 for India, China, Australia New Zealand, Ozeania, Pazific Ocean
- 97.6W INMARSAT 4‑F3 for North and South America
Inmarsat services
The Inmarsat satellites currently cover the following services via L‑band frequencies:
- Voice
GSPS (Global Satellite Phone Service) is the telephone service for the satellite phones IsatPhone Pro and IsatPhone 2 on land and at sea. - Internet (Land)
BGAN (Broadband Global Area Network) is a solution for mobile broadband internet access and telephony on land. BGAN HDR and BGAN LINK are also part of these services. - Machine control
BGAN M2M (Machine to Machine) - Internet (Sea)
FleetOne, FleetBroadband (FBB), Inmarsat C (GMDSS, SOLAS compliant) are solutions for mobile broadband internet access and telephony at sea. - Internet (Aircraft)
Swift Broad Band is a solution for mobile broadband Internet access and telephony on aircraft.
About the history of Inmarsat
Inmarsat was created in 1979 from the INternational MARitime SATellite Organization initiative of the International Maritime Organization (IMO) to improve civil (security) communications at sea, especially to provide coverage in regions that were not covered by short or medium wave.
At first, leased satellites were used, then from 1983 only own satellites. In 1984, the name changed to International Mobile Satellite Organization, and in 1999, the organization was privatized as Inmarsat plc, headquartered in London, and placed under the control of IMSO (International Mobile Satellite Organization). The company has been listed on the stock exchange since 2005. In 2019, the Inmarsat Group was acquired by Connect Bidco Limited, registered in Guernsey. Since 2011 Inmarsat is a part of US american company Viasat Inc.


